The Play of Light in a Diamond
Aside from its extreme hardness, the diamond is characterized by a number of distinctive properties:
Almost all diamonds contain foreign atoms. The most commonly occurring example of this is nitrogen, which is responsible for a yellow colour tinge that is visible in many stones. A perfectly pure diamond is completely colourless and non-fluorescent.
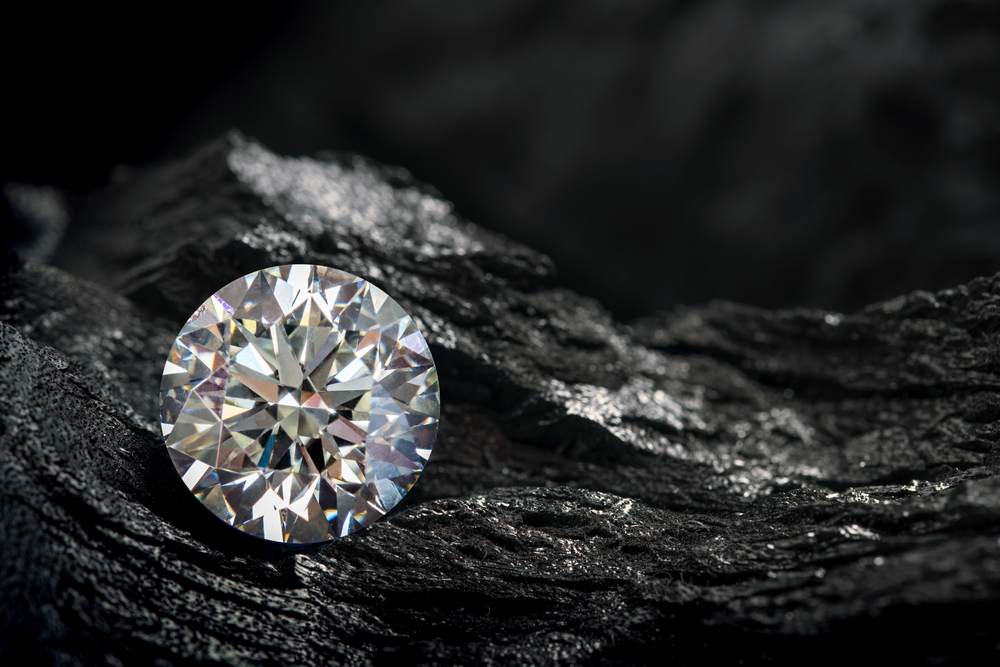

Transparency
The transparency of a diamond varies from completely clear to completely opaque. Only the clear stones are used in jewellery. Other diamonds are used for various, although usually industrial purposes. A stone that does not sparkle after it has been cut and polished is known as a “dead” stone.
Clarity
Pure diamonds are extremely rare. Almost all rough diamonds contain impurities or “inclusions,” which are traces of non-diamond materials that were ‘trapped’ in the mineral during the stone’s formation. Many inclusions are removed during the cleaving, sawing, cutting and polishing of the diamond.
Brilliance
In general, rough diamond is not particularly attractive; it barely sparkles. The diamond only achieves its characteristic, stunning brilliance after it has been polished. The diamond’s unusual attractiveness and play of colour is due to its reflectivity and exceptionally high refractive index, by which the light is optimally “broken”. The result is a dispersion of the white light into all the colours of the rainbow. Of course, all the facets of a polished diamond have to be oriented properly for this effect to be obtained. Only then does the stone come to life.
Colour
Most diamonds are referred to as “colourless,” which in diamond terminology ranges from really colourless to yellowish. A small percentage of diamonds have a distinctive colour—from yellow to black, through blue, green, pink and even red. In this respect they resemble coloured gemstones. These so-called “fancy colours” are very rare and highly desirable. Since their intense appearance is fashionable, colour is sometimes produced artificially using modern technology. Artificially coloured diamonds are less valuable than naturally coloured diamonds.

Fluorescence
Like other gemstones, a large number of diamonds radiate visible light when exposed to ultraviolet light. This fluorescence is usually blue, but it can also be white, violet and sometimes yellow, green or orange.